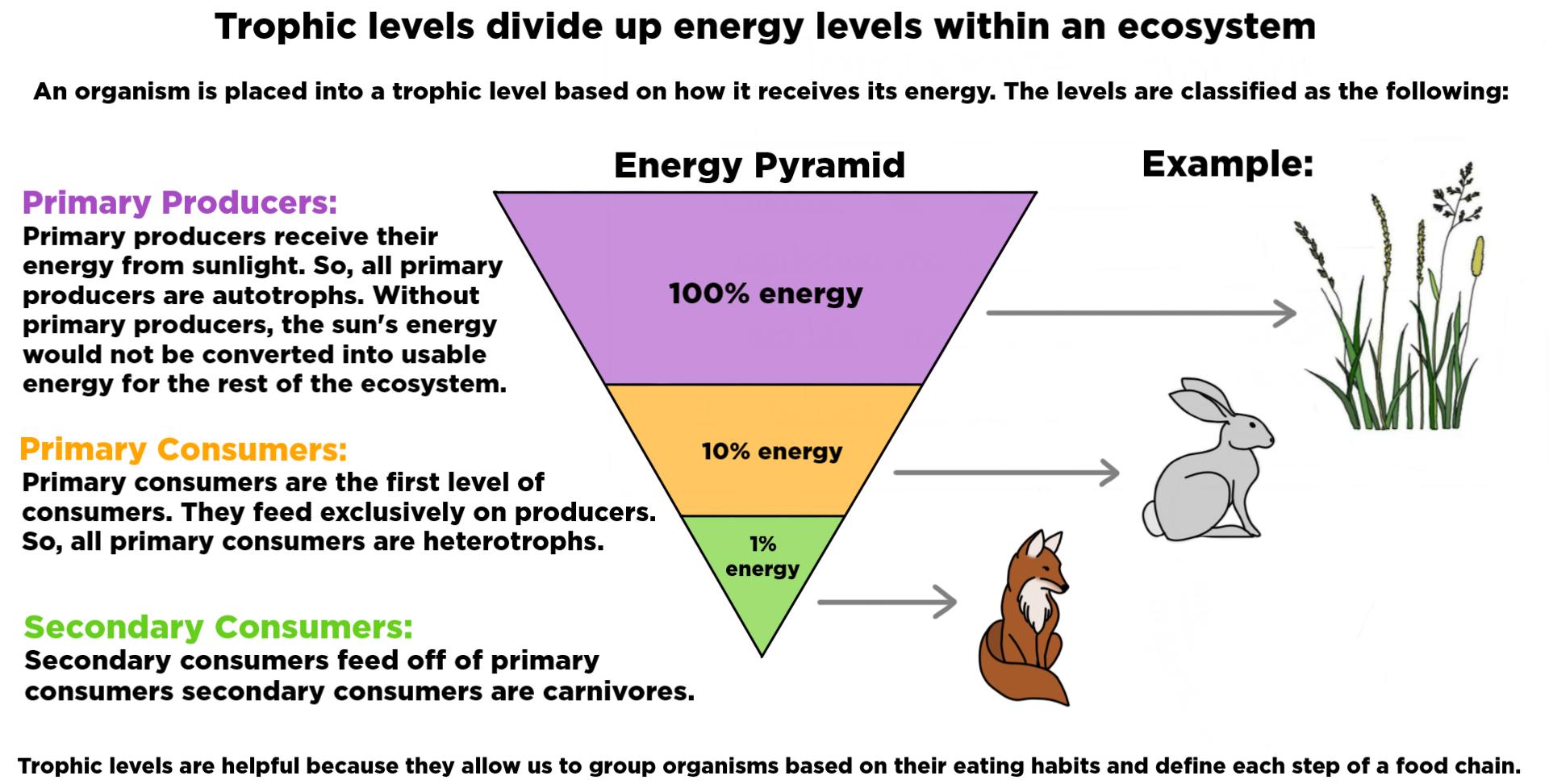
Chapter 3 Ecosystem Ecology Biology Diagrams Trophic level, any step in a nutritive series, or food chain, of an ecosystem. Organisms are classified into levels on the basis of their feeding behavior. The lowest level contains the producers, green plants, which are consumed by second-level organisms, herbivores, which, in turn, are consumed by carnivores.

Learn what a trophic level is and how it relates to the food chain in an ecosystem. Find out the five main trophic levels and their characteristics, from primary producers to apex predators, with examples of each.

Trophic Level (Food Chain & Web): Definition & Examples ... Biology Diagrams
The trophic level of an organism is the position it occupies in a food web.Within a food web, a food chain is a succession of organisms that eat other organisms and may, in turn, be eaten themselves. The trophic level of an organism is the number of steps it is from the start of the chain. A food web starts at trophic level 1 with primary producers such as plants, can move to herbivores at
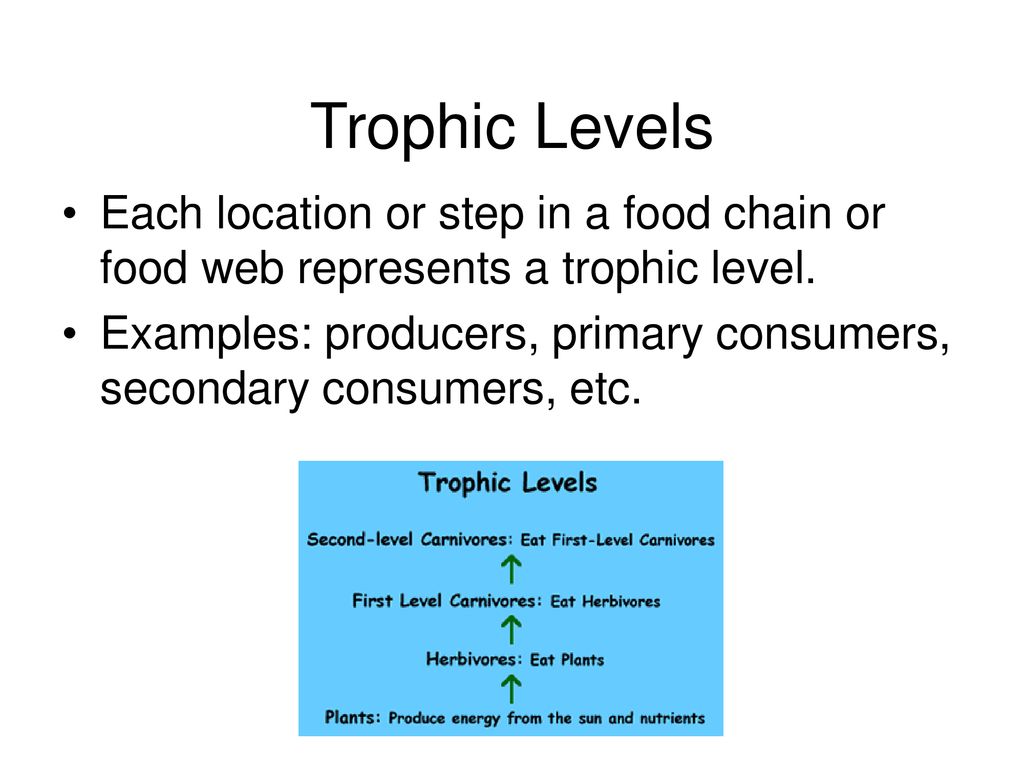
The second trophic level in all food chains is an herbivore or omnivore close omnivore An animal that eats both plants and meat. called a primary consumer. Mosquito larvae are the primary
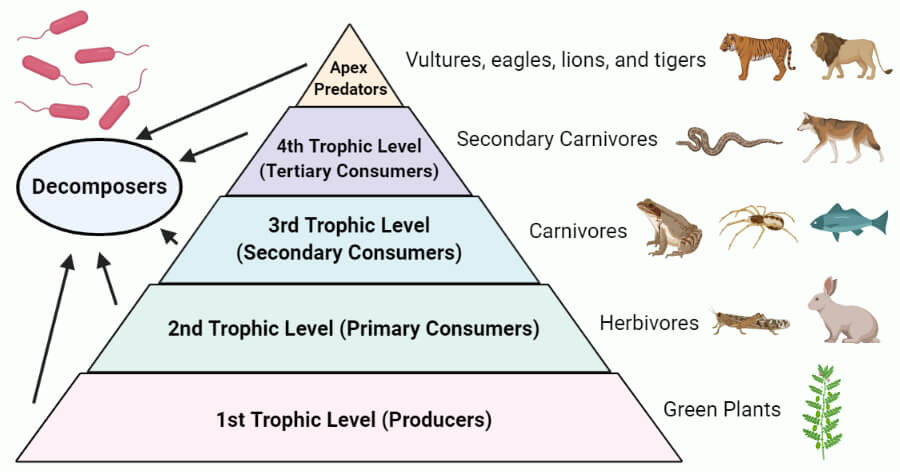
Trophic Levels, Food Chains, Interactions Biology Diagrams
Ecosystem - Trophic Levels, Food Chains, Interactions: Together, the autotrophs and heterotrophs form various trophic (feeding) levels in the ecosystem: the producer level (which is made up of autotrophs), the primary consumer level (which is composed of those organisms that feed on producers), the secondary consumer level (which is composed of those organisms that feed on primary consumers